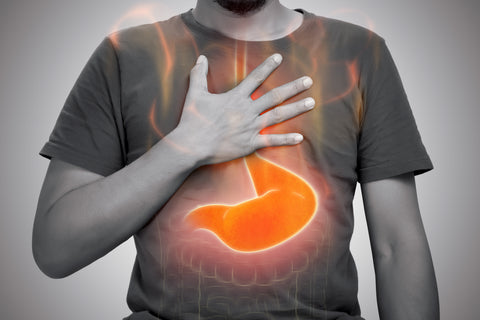
Heartburn is a common symptom, especially during fasting. Statistics indicate that more than five million people worldwide suffer from it daily, at the very least.
What is heartburn?
Heartburn is a condition where individuals feel a burning sensation in their chest that may also extend to their throat. It happens when stomach acid rises and reaches the esophagus. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to close completely, which results in recurring discomfort after eating or lying down. This article will primarily discuss heartburn caused by food.
How to overcome heartburn?
Don't let heartburn keep you from enjoying your favorite meals this Ramadan. Follow these health tips.
You'll notice an improvement in heartburn symptoms by avoiding or reducing the intake of the following food triggers:
- Caffeine: Whether in coffee, tea, or energy drinks.
- Chocolate.
- Spicy foods.
- Foods high in fat.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Mint.
- Tomato and Ketchup.
Tip: Replace coffee, tea, and carbonated drinks with water, especially during suhoor (pre-dawn meal) and Iftar. You'll notice an improvement or disappearance of symptoms.
- Avoid starting your iftar with a heavy dish. Always begin with a light meal, such as whole grains, vegetables, or fruits, and reduce consumption of bread and Carbohydrates.
- Avoid lying down or reclining immediately after eating. If you must, don't lie directly on your back and elevate your head.
- Avoid drinking large amounts of water before meals; select moderate sips distributed over longer intervals.
- Prevent mouth dryness to stimulate saliva production. Consider using sugar-free gum or lozenges.
- Refrain from smoking.
- Try breathing slowly and correctly.
- It is advisable to avoid wearing tight clothing and belts that put pressure on your stomach.
- Work on reducing excess weight; the closer you are to an ideal weight, the lower the chances of heartburn.
It's worth noting that the above recommendations are effective for mild to rarely occurring heartburn. However, medical treatments may be necessary if symptoms become bothersome and recurrent. These include:
- If your symptoms don't occur more than once a week, consider the following:
- Antacids: containing magnesium or aluminum hydroxide, which neutralize stomach acid within five minutes and remain effective for half an hour to a full hour.
- Sucralfate or alginate compounds: provide quick relief by forming a protective layer against stomach acid within seconds e.g sodium alginate.
- If symptoms occur more than twice a week, you may need the following:
- Histamine H2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs): prevent histamine-2 receptors on parietal cells from secreting acid. Examples include cimetidine, famotidine, and nizatidine.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): inhibit a crucial step in stomach acid production by parietal cells. PPIs are given for chronic conditions and include esomeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole and omeprazole.
FAQs about heartburn:
What is the fastest treatment for heartburn?
As mentioned previously, antacids and alginates are quick-acting and don't require a prescription.
How long does heartburn last?
It is assumed that the duration of the symptoms can vary from a few minutes to several hours, depending on how long it takes for the stomach to empty its contents. Mild to moderate cases usually do not persist for extended periods.
Is heartburn serious?
If acid reflux is recurring and affecting your daily routine, it's advisable to consult a doctor, as it may develop into gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
How do I differentiate between heartburn and indigestion?
Indigestion and heartburn are two separate conditions, but they can occur simultaneously. Indigestion refers to the discomfort or pain in the stomach along with a burning sensation after consuming food or drink. Common symptoms include a feeling of fullness and bloating. Probiotic supplements can help alleviate these symptoms.













Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!